Effort
Effort
Effort is one of the cornerstones of accurate training planning and form determination in Tredict and can be calculated from 3 different input values - wattage, heart rate and speed. In turn, the calculated effort is the input value for your form curve and is intended to interact with this form curve. The effort amount also indicates at a glance how effortful an activity was. To summarise, you can later see in the evaluation and also the form curve over a certain period of time whether the effort has been increased or decreased and adjust your further training or that of an athlete accordingly.
The Tredict effort offers a high level of configurability with high expressiveness at the same time.

Redundant effort calculation
The effort calculation is designed redundantly in Tredict. Tredict essentially calculates the effort from 3 different data sources. The time series recorded by your device will be used in the order you have specified.
- Power
- Heart rate
- Speed
Regardless of the source from which the effort was calculated, the effort from wattage, heart rate or speed should be approximately the same in theory. The underlying calculations are designed for comparability; after all, the effort is the input value for your form curve, regardless of the zone type used for calculation. To do this, however, you need correctly set capacity values and a zone model for all zone types that is up to date. In practice, this is usually not relevant, as you often decide on a zone type, e.g. "Running by heart rate".
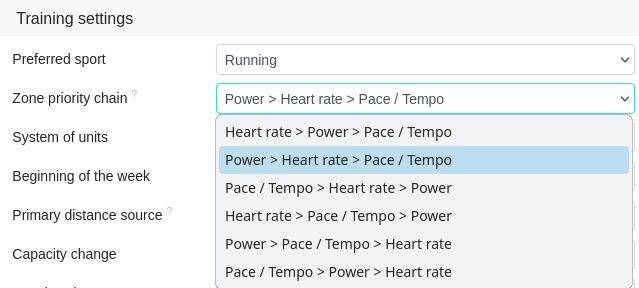
Zone priority chain
Specify which zone priority chain you prefer in the general settings. If you train with a power meter, you could set the zone priority chain to 'wattage -> heart rate -> speed'. If the wattage is not available for a certain reason, the effort is calculated from the next zone type, the heart rate.
Effort factors
The effort of an activity is influenced by 4 factors.
- Active Duration - The longer the activity, the higher the effort.
- One of the 3 performance values - heart rate, wattage or speed.
- Zone Intensity - A higher intensity range increases effort over the same time.
- Capacity - Maximum heart rate, FTP, FTPa
To summarise:
The longer the activity, the greater the effort required. The more intensive the activity, the greater again the effort required. A long and intensive activity, e.g. a half marathon competition, therefore requires a great deal of effort.
Effort tracking
Per second effort for executed activities
Your recording device records the time series at one-second intervals. Tredict calculates a "micro effort" for every second, looks at the current input value at this time interval, e.g. 180 watts, calculates a base effort and multiplies this again by an intensity factor. The intensity factor is determined indirectly by your zone settings. If the input value falls into a zone range with high intensity, the factor is correspondingly higher.
The micro-efforts are totalled over the period of the activity, resulting in the total effort of the activity.
Effort of planned training sessions from the segments
The effort of planned structured workouts is not calculated from the second-by-second data, but from the planned segments according to the same principle. The zone priority chain also applies here. If a structured workout maps 2 different zone types in the segments, e.g. a segment by heart rate and a segment by speed, then the effort is only calculated from the heart rate segment if the heart rate is prioritised. It is therefore possible to enter the target values for all zone types simultaneously for sections that work with "Target value", so that the effort can be calculated accurately.
Capacity range
Your available capacity also plays a role in calculating the effort. The FTP is integrated into the calculation for the wattage, the FTPa for the speed and the range between resting heart rate and maximum heart rate for the heart rate.
For an accurate effort calculation, it is important that you know your capacity values.
You can specify the capacity values "maximum heart rate" or the "FTP or FTPa" by editing or adding a new capacity revision under "Zones & Capacity".
Gender-specific effort
For female athletes, the calculated effort is automatically increased by 20%. The increase results from a comparison of the world-class lists in athletics. Without this gender-specific correction factor, the shape curve would not behave correctly.
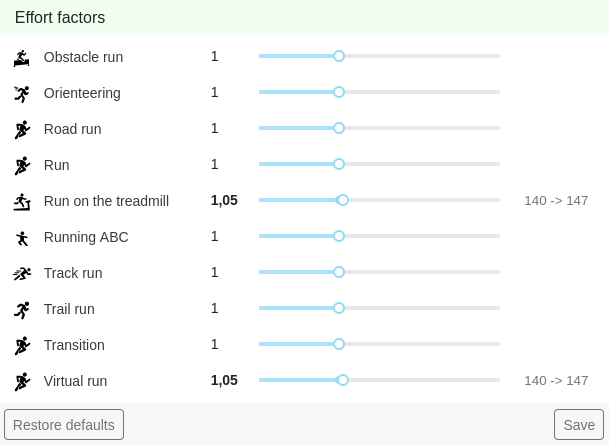
Manual effort correction factors
Tredict offers you the option of setting a manual correction factor for individual sport variants. For example, running on a treadmill is generally much more strenuous than running in nature due to the lack of air cooling. Tredict has already preset the correction factor to 1.05 here. You can find the correction factors under the settings for "Zones & capacity".
Please use this function with caution. Usually no settings need to be made here.
Comparability with other platforms
The Tredict effort has some advanced features, described in this category, that make a comparison with other effort metrics, such as the TSS® from TrainingPeaks or the Strava effort, not meaningful. If the effort is harmonised with other platforms, the Tredict effort would lose its special significance, which includes, for example, high intensities or gender specificity.
An effort, regardless of the platform, is always a relative value that is only comparable in itself as long as the calculation basis is the same. Of course you can compare the Tredict effort with other Tredict athletes.
It is important that you, as an athlete or as a coach, get a feeling for this relative value so that you can compare it with itself.
Calculate other platforms effort with the help of custom fields
If you do not want to do without the TSS® from TrainingPeaks and you have found the calculation formula for it, you can programme in the corresponding formula under "Settings" -> " Custom fields". The custom field created is then displayed for all activities and appears in the evaluation. Tredict is of course not responsible for the creation of your custom fields, which are not calculated on the Tredict servers.